Discover what a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is, how it works, its types, benefits, and whether it’s the right car for you in 2025. Full guide + FAQ!
What is a Hybrid Electric Vehicle?
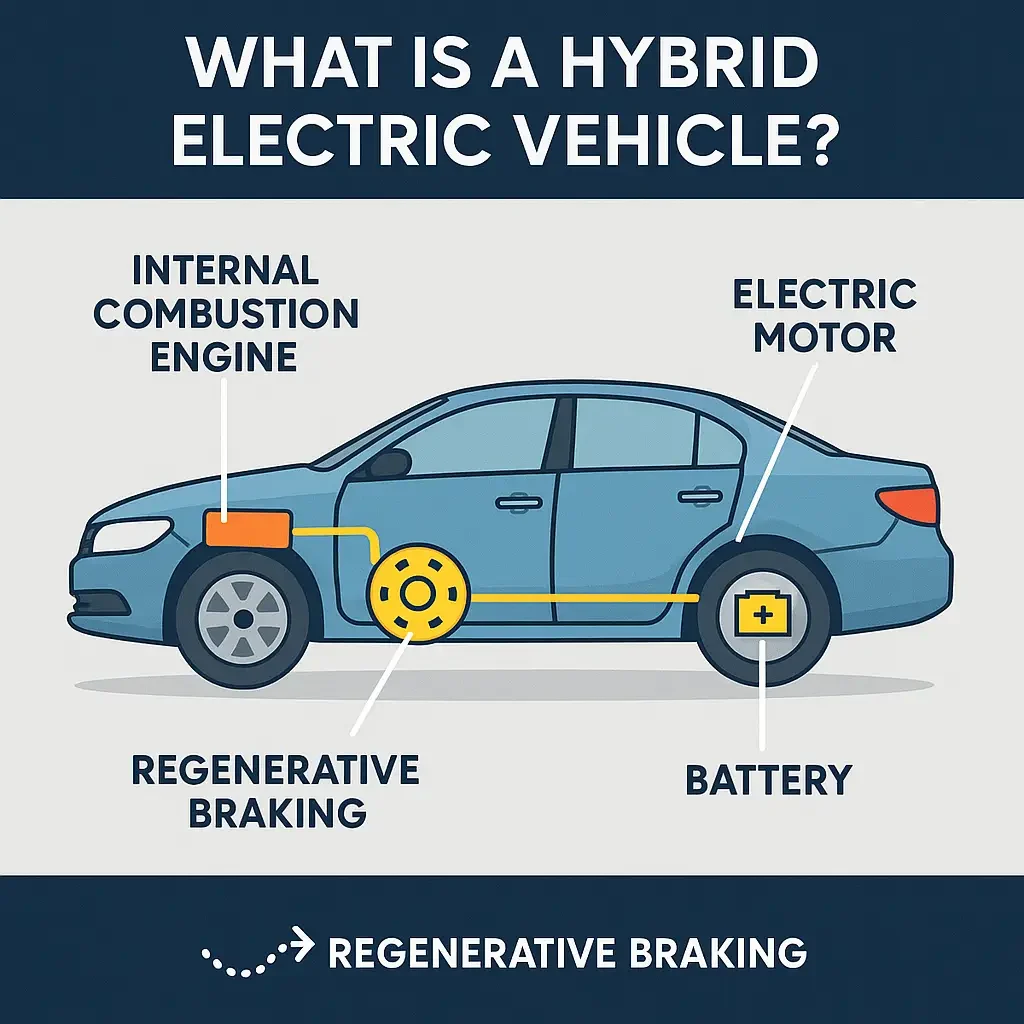
A Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) is a type of car that combines two sources of power: a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor powered by a battery. Unlike fully electric vehicles, hybrid cars don’t rely solely on electricity. Instead, they intelligently switch or combine power from the engine and motor for maximum efficiency.
The goal? Better fuel economy, lower emissions, and a smoother driving experience.
HEVs differ from plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) and battery electric vehicles (BEVs) primarily in that they do not need to be plugged in. Instead, the battery charges while you drive—often through regenerative braking.
What is a Hybrid Car?
Put simply, a hybrid car is a vehicle that uses more than one type of power. It blends the strengths of gasoline and electricity, creating a ride that’s efficient, cleaner, and ideal for modern-day commuting.
Hybrid cars are gaining popularity not just for their eco-friendly image but for practical benefits like reduced fuel consumption and lower carbon footprints.
What Does a Hybrid Car Mean?
The term “hybrid” refers to the fusion of two energy sources. In this context, it means a vehicle using both a fuel-driven engine and an electric motor. This combination leads to:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Improved fuel economy
- Lower operational costs
It’s the automotive industry’s middle ground between conventional fuel vehicles and full-electric models.
How Does a Hybrid Car Work?
A hybrid car typically works through a dynamic interaction between the gasoline engine and the electric motor. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Starting/Low Speed: The car runs primarily on electric power.
- Acceleration: Both electric and gasoline engines may work together.
- Cruising: The gasoline engine takes over.
- Braking or Deceleration: Energy is captured and stored in the battery (regenerative braking).
This smart distribution of energy is what makes hybrid cars both fuel-efficient and smooth to drive.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) Working Mechanism
Hybrid Electric Vehicles use an Electric Motor Drive System along with a power control unit that manages the flow of electricity. Here’s how:
| Mode | Power Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Electric-Only | Battery | Ideal for city driving at low speeds |
| Gasoline-Only | Engine | Best for highway speeds |
| Hybrid Mode | Both | Optimized for acceleration and efficiency |
| Regenerative Mode | Braking System | Converts kinetic energy into electric energy |
Types of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Series Hybrid
- The engine charges the battery; the wheels are powered only by the electric motor.
- Parallel Hybrid
- Both engine and electric motor drive the wheels together.
- Plug-In Hybrid (PHEV)
- Larger battery, can be charged externally; operates more like a full EV for short trips.
Hybrid Car Engine: Inside the Technology
The hybrid engine is designed to work with two systems:
- The gas engine provides primary propulsion at higher speeds.
- The electric motor assists with torque during acceleration and takes over at lower speeds.
Advanced computers coordinate both systems, ensuring a seamless transition and maximizing fuel economy.
Hybrid Car Battery: Power and Efficiency
Batteries in HEVs are typically nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) or lithium-ion (Li-ion).
Key features:
- Recharge automatically via regenerative braking.
- Last 8–10 years on average.
- Covered by manufacturer warranties.
While replacement can be costly, the savings in fuel and maintenance often balance it out.
Toyota Hybrid Cars: A Pioneer in the Industry
Toyota has been a trailblazer in hybrid technology, with its Prius being the world’s first mass-produced HEV. Today, the lineup includes:
- Toyota Prius
- Toyota Corolla Hybrid
- Toyota RAV4 Hybrid
- Toyota Camry Hybrid
Toyota hybrids are known for durability, fuel economy, and resale value.
Hybrid Cars in the UK
Hybrid vehicles in the UK are rapidly gaining popularity due to:
- ULEZ exemptions in London
- Government grants for plug-in hybrids
- Increasing fuel prices
Popular models include the Honda Jazz Hybrid, Toyota Yaris Hybrid, and Kia Niro Hybrid.
Hybrid Cars in the US
In the US, HEVs are being adopted due to:
- Federal tax incentives
- High gas prices
- Growing concern for climate change
Top picks include the Ford Escape Hybrid, Toyota Highlander Hybrid, and Honda Accord Hybrid.
List of Top Hybrid Electric Vehicles in 2025
| Model | Type | Fuel Efficiency (MPG) |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota Prius | HEV | 58 city / 53 highway |
| Hyundai Ioniq | HEV | 59 city / 58 highway |
| Ford Maverick | HEV | 42 city / 33 highway |
| Honda CR-V Hybrid | HEV | 40 city / 34 highway |
Hybrid Electric Vehicle Prices and Value
Prices vary depending on the model and type. On average:
- Basic HEV: $25,000 – $30,000
- Mid-range PHEV: $30,000 – $40,000
- Luxury Hybrids: $50,000+
While upfront costs may be higher, fuel savings and incentives often make them cost-effective in the long run.
Pros and Cons of Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Pros:
- Lower emissions
- Improved fuel efficiency
- Smooth, quiet ride
- Tax credits
Cons:
- Higher purchase price
- Battery replacement cost
- Complex maintenance
Advantages of Driving a Hybrid Car
- Eco-friendly: Reduces pollution and fuel dependency.
- Savings: Reduced fuel and maintenance costs.
- Performance: Immediate torque, smooth ride.
Disadvantages and Challenges of HEVs
- Initial cost: Higher than non-hybrid counterparts.
- Limited range (for some hybrids).
- Battery disposal: Requires careful recycling.
The Future of Hybrid Technology
The future looks promising with:
- Solar-assisted charging
- Hydrogen hybrids
- AI-powered efficiency systems
Hybrid cars will remain a vital transition technology until full EV adoption is feasible worldwide.
FAQs About Hybrid Electric Vehicles
1. What is a hybrid electric vehicle?
A car that uses both a gasoline engine and electric motor for power, offering better efficiency and lower emissions.
2. How does a hybrid car work?
It switches between or combines gas and electric power depending on speed, terrain, and acceleration needs.
3. Do hybrid cars need to be charged?
HEVs do not. Only Plug-In Hybrids (PHEVs) require external charging.
4. How long does a hybrid car battery last?
Typically 8–10 years or 100,000–150,000 miles.
5. Are hybrid vehicles worth it?
Yes—especially for city drivers who benefit most from electric-only operation and fuel savings.
6. What is the difference between a hybrid and an electric car?
A hybrid uses both gas and electricity; an electric car runs only on battery power.




